|
|
|
|
---
|
|
|
|
|
Activity
|
|
|
|
|
---
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#### 目录
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. 思维导图
|
|
|
|
|
2. 概述
|
|
|
|
|
3. 生命周期
|
|
|
|
|
- 正常情况下的生命周期(注意透明 Activity 和 DialogActivity)
|
|
|
|
|
- 异常情况下的生命周期
|
|
|
|
|
4. 启动模式
|
|
|
|
|
- LaunchMode
|
|
|
|
|
- standard
|
|
|
|
|
- singleTop
|
|
|
|
|
- singleTask
|
|
|
|
|
- singleInstance
|
|
|
|
|
- Intent.Flags
|
|
|
|
|
- FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK
|
|
|
|
|
- FLAG_ACTIVITY_SINGLE_TOP
|
|
|
|
|
- FLAG_ACTIVITY_CLEAR_TOP
|
|
|
|
|
- FLAG_ACTIVITY_EXCLUDE_FORM_RECENTS
|
|
|
|
|
5. IntentFilter 匹配规则
|
|
|
|
|
- action
|
|
|
|
|
- category
|
|
|
|
|
- data
|
|
|
|
|
- URI
|
|
|
|
|
- mimeType
|
|
|
|
|
6. 重要方法
|
|
|
|
|
- onSaveInstanceState、onRestoreInstanceState
|
|
|
|
|
- startActivityForResult
|
|
|
|
|
- onNewIntent
|
|
|
|
|
- onConfigurationChanged
|
|
|
|
|
- onTirmMemory
|
|
|
|
|
7. 转场动画
|
|
|
|
|
- overridePendingTransition
|
|
|
|
|
- 设置 Application Stype
|
|
|
|
|
- ActivityOptions
|
|
|
|
|
8. 启动流程
|
|
|
|
|
1. Launcher 请求 AMS
|
|
|
|
|
2. AMS 到 ApplicationThread 的调用过程
|
|
|
|
|
3. ActivityThread 启动 Activity
|
|
|
|
|
9. 参考
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#### 思维导图
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
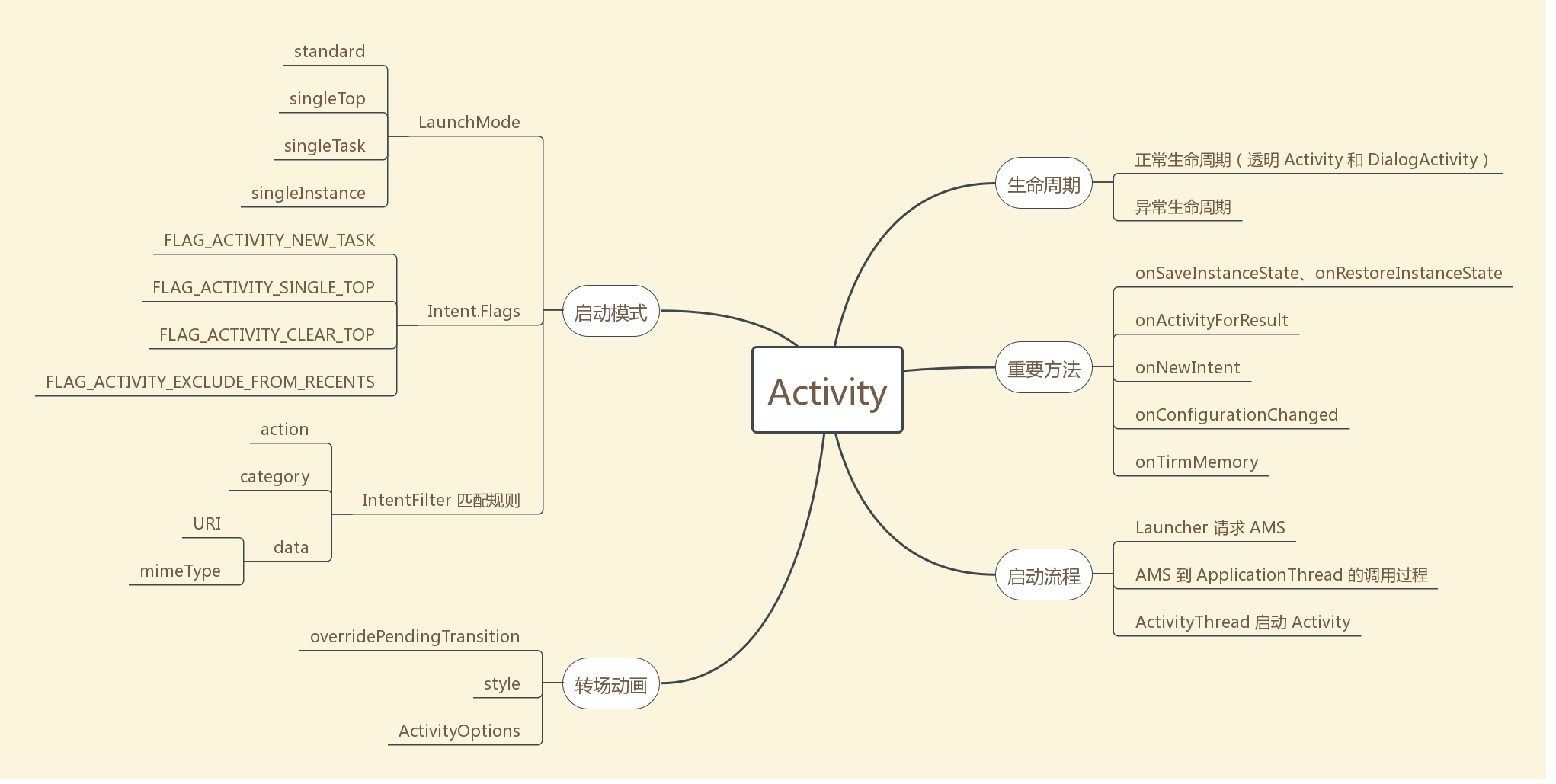
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#### 概述
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Activity 即用户界面。
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#### 生命周期
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
说到生命周期,最经典的一张图:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
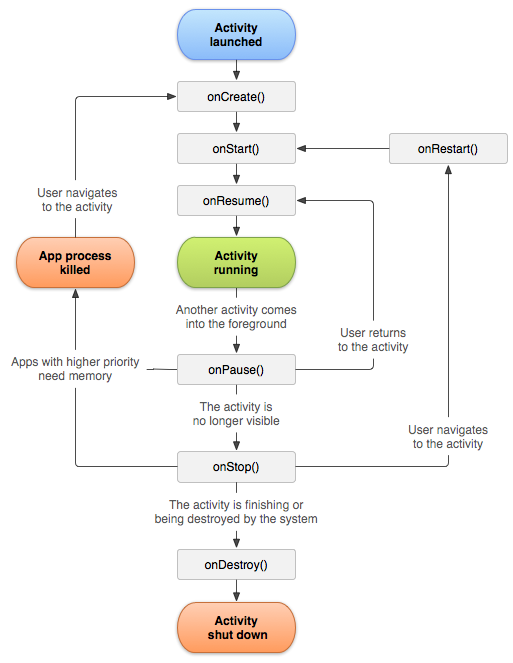
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
不过还是说一下实例会更好理解一下:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 情况 | 回调 |
|
|
|
|
|
| ----------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
|
|
|
|
| 第一次启动 | onCreate 、onStart、onResume |
|
|
|
|
|
| 从 A 跳转到不透明的 B | A_onPause、B_onCreate、B_onStart、B_onResume、A_onStop |
|
|
|
|
|
| 从 A 跳转到透明的 B | A_onPause、B_onCreate、B_onStart、B_onResume |
|
|
|
|
|
| 从不透明的 B 再次回到 A | B_onPause、A_onRestart、A_onStart、A_onResume、B_onStop、B_onDestory |
|
|
|
|
|
| 从透明的 B 再次回到 A | B_onPause、A_onResume、B_onStop、B_onDestory |
|
|
|
|
|
| 用户按 home 键 | onPause、onStop |
|
|
|
|
|
| 按 home 键回到应用 | onRestart、onStart、onResume |
|
|
|
|
|
| 用户按 back 键会退 | onPause、onStop、onDestory |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
透明 Activity 和 DialogActivity 类似,在跳到 DialogActivity 也不会回调前一个 Activity 的 onStop 方法。
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#### 启动模式
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
##### LaunchMode
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 启动模式 | 说明 |
|
|
|
|
|
| -------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
|
|
|
|
| standard | 标准模式,也是系统的默认模式,每次启动一个 Activity 都会重新创建一个实例 |
|
|
|
|
|
| singleTop | 栈顶复用,如果新 Activity 已经位于任务栈的栈顶,那么此 Activity 不会被重新创建,同时它的 onNewIntent 方法会被回调 |
|
|
|
|
|
| singleTask | 栈内复用,只要 Activity 在一个栈中存在,那么多次启动此 Activity 都不会重新创建实例,和 singleTop 一样,系统也会回调其 onNewIntent |
|
|
|
|
|
| singleInstance | 单例模式,启动的 Activity 会创建一个新的任务栈并压入栈中,由于栈内复用的特性,后续的请求均不会创建新的 Activity,除非这个任务栈被系统销毁了 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 情况 | 回调 |
|
|
|
|
|
| ------------------------------------------------------------ | ------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
|
|
|
|
| 从 A(singleTask)startActivity B(standard),B startActivity A | 第一步:A_onPause、B_onCreate、B_onStart、B_onResume、A_onStop 第二步:B_onPause、A_onNewIntent、A_onRestart、A_onStart、A_onResume、B_onStop、B_onDestory |
|
|
|
|
|
| 在 A (singleTask)startActivity A | A_onPause、A_onNewIntent、A_Resume |
|
|
|
|
|
| 在 A (singleTop)startActivity A | A_onPause、A_onNewIntent、A_Resume |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
在 singleTask 启动模式中,多次提到某个 Activity 所需的任务栈,什么是 Activity 所需要的任务栈呢?这就要从一个参数说起:taskAffinity,任务相关性。这个参数标识了一个 Activity 所需要的任务栈的名字,默认情况下,所有 Activity 所需的任务栈的名字为应用的包名。当然,我们可以为每个 Activity 都单独指定 taskAffinity 属性,这个属性值必须不能和包名相同,否则相当于没有设置。taskAffinity 属性主要和 singleTask 启动模式和 allowTaskReparenting 属性配对使用,在其他情况下没有意义。
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
taskAffinity 与 singleTask 配对使用:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
如果启动了设置了这两个属性的 Activity,这个 Activity 就会在 taskAffinity 设置的任务栈中。
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
taskAffinity 与 allowTaskReparenting 配对使用:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
当一个应用 A 启动了应用 B 的某个 Activity 后,如果这个 Activity 的 allowTaskReparenting 属性为 true 的话,那么当应用 B 被启动后,此 Activity 会直接从应用 A 的任务栈转移到应用 B 的任务栈中。这个属性主要作用就是将这个 Activity 转移到它所属的任务栈中,例如一个短信应用收到一个带有网络链接的短信,点击链接会跳到浏览器,这时候如果 allowTaskReparenting 设置为 true 的话,打开浏览器应用就会直接显示刚才打开的网页页面,而打开短信应用后这个浏览器界面就会消失。
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
启动模式了解之后,那是如何指定启动模式的方式呢?
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
有两种:一种是在 AndroidMenifet 文件设置 launchMode 属性,一种是给 Intent 设置 Flag。
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
如果两者都存在,后者优先级更高。
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
##### Activity 中的 Flags
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 标记位 | 说明 |
|
|
|
|
|
| ---------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
|
|
|
|
| FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK | 为 Activity 指定 singleTask 启动模式,其效果和在 xml 中指定启动模式相同 |
|
|
|
|
|
| FLAG_ACTIVITY_SINGLE_TOP | 为 Activity 指定 singleTop 启动模式,其效果和在 xml 中指定启动模式相同 |
|
|
|
|
|
| FLAG_ACTIVITY_CLEAR_TOP | 具有此标记位的 Activity,当启动它时,同一个任务栈中所有位于它上面的 Activity 都要出栈。这个模式一般需要和 FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK 配合使用,在这种情况下,被启动的 Activity 实例如果已经存在,那么系统就会调用它的 onNewIntent。如果被启动的 Activity 采用 standard 模式启动,那么它连同它之上的 Activity 都要出栈,系统会创建新的 Activity 实例并放入栈顶 |
|
|
|
|
|
| FLAG_ACTIVITY_EXCLUDE_FROM_RECENTS | 具有这个标记的 Activity 不会出现在历史的 Activity 的列表中,当某些情况下我们不希望用户通过历史列表回到我们的 Activity 的时候这个标记比较有用。它等同于在 xml 中指定 Activity 的属性 android:excludeFormRecents="true" |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#### IntentFilter 的匹配规则
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
启动 Activity 分为两种,显式调用和隐式调用。显式调用就不多说了,隐式调用需要 Intent 能够匹配目标组件的 IntentFilter 中所设置的过滤信息,如果不匹配将无法启动目标 Activity。IntentFilter 的过滤信息有 action、category、data。
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IntentFilter 需要注意的地方有以下:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. 一个 Activity 中可以有多个 intent-filter
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2. 一个 intent-filter 同时可以有多个 action、category、data
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3. 一个 Intent 只要能匹配任何一组 intent-filter 即可启动对应 Activity
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4. 新建的 Activity 必须加上以下这句,代表能够接收隐式调用
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
```java
|
|
|
|
|
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
##### action 的匹配规则
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
action 的匹配规则就是只要满足其中一个 action 就可以启动成功。
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
```xml
|
|
|
|
|
<activity android:name=".activity.SecondActivity" >
|
|
|
|
|
<intent-filter>
|
|
|
|
|
<action android:name="demo"/>
|
|
|
|
|
<action android:name="demo2"/>
|
|
|
|
|
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT"/>
|
|
|
|
|
</intent-filter>
|
|
|
|
|
</activity>
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
```java
|
|
|
|
|
Intent intent = new Intent();
|
|
|
|
|
intent.setAction("demo");
|
|
|
|
|
startActivity(intent);
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
注意,action 是区分大小写的。
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
##### category 匹配规则
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
category 在代码设置如下:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
```java
|
|
|
|
|
intent.addCategory("")
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
这句可以添加也可以不添加,因为代码默认会为我们匹配 “android:intent.category.DEFAULT”。
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
##### data 匹配规则
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
data 主要是由 URI 和 mimeType 组成的。URI 的结构如下:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
<scheme>://<host>:<port>[<path>|<pathPrefix>|<pathPattern>]
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
语法如下:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
```xml
|
|
|
|
|
<data android:scheme="string"
|
|
|
|
|
android:host="string"
|
|
|
|
|
android:port="string"
|
|
|
|
|
android:path="string"
|
|
|
|
|
android:pathPattern="string"
|
|
|
|
|
android:pathPrefix="string"
|
|
|
|
|
android:mimeType="string" />
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
实例:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
```java
|
|
|
|
|
<activity android:name=".activity.SecondActivity" >
|
|
|
|
|
<intent-filter>
|
|
|
|
|
<action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW"/>
|
|
|
|
|
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT"/>
|
|
|
|
|
<data
|
|
|
|
|
android:host="omooo"
|
|
|
|
|
android:port="80"
|
|
|
|
|
android:scheme="demo"/>
|
|
|
|
|
</intent-filter>
|
|
|
|
|
</activity>
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
```java
|
|
|
|
|
Intent intent = new Intent();
|
|
|
|
|
intent.setData(Uri.parse("demo://omooo:80/data?age=18&sex=girl"));
|
|
|
|
|
if (getPackageManager().resolveActivity(intent, PackageManager.MATCH_DEFAULT_ONLY) != null) {
|
|
|
|
|
startActivity(intent);
|
|
|
|
|
} else {
|
|
|
|
|
Toast.makeText(this, "Activity Not Found", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
这里,注意我用了 PackageManager#resolverActivity() 来判断是否存在该隐式 Activity,这样就避免找不到 Activity 而导致应用 Crash。同时注意,第二个参数必须传 PackageManager.MATH_DEFAULT_ONLY,因为只有 category 为 DEFAULT 的 Activity 才能接收隐式启动。
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
```java
|
|
|
|
|
if (getIntent().getData() != null) {
|
|
|
|
|
Uri uri = getIntent().getData();
|
|
|
|
|
String scheme = uri.getScheme();
|
|
|
|
|
Log.i(TAG, "scheme: " + scheme);
|
|
|
|
|
String host = uri.getHost();
|
|
|
|
|
Log.i(TAG, "host: " + host);
|
|
|
|
|
int port = uri.getPort();
|
|
|
|
|
Log.i(TAG, "port: " + port);
|
|
|
|
|
String path = uri.getPath();
|
|
|
|
|
Log.i(TAG, "path: " + path);
|
|
|
|
|
String query = uri.getQuery();
|
|
|
|
|
Log.i(TAG, "query: " + query);
|
|
|
|
|
Set<String> params = uri.getQueryParameterNames();
|
|
|
|
|
for (String item : params) {
|
|
|
|
|
Log.i(TAG, "item: " + item + " value: " + uri.getQueryParameter(item));
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
//输出:
|
|
|
|
|
Demo_SecondActivity: scheme: demo
|
|
|
|
|
Demo_SecondActivity: host: omooo
|
|
|
|
|
Demo_SecondActivity: port: 80
|
|
|
|
|
Demo_SecondActivity: path: /data
|
|
|
|
|
Demo_SecondActivity: query: age=18&sex=girl
|
|
|
|
|
Demo_SecondActivity: item: age value: 18
|
|
|
|
|
Demo_SecondActivity: item: sex value: girl
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
说完 URI,剩下的 mimeType 表示要传递的数据类型,通常是 text/plain 或 image/jpeg 等等。
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
```java
|
|
|
|
|
intent.setType("text/plain");
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
不过需要注意的是,如果同时设置了 URI 和 mimeType 的话就必须使用以下代码才能跳转:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
intent.setDataAndType(Uri.parse("demo://omooo"),"text/plain")
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
因为如果使用 setData() 或者 setType() 的话,分别会将相应的 type 和 data 置为 null。
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#### 重要方法
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. onSaveInstanceState()、onRestoreInstanceState()
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
这两个方法只有在应用遇到意外情况下才会触发,比如横竖屏切换,可以用于保存一些临时性数据。
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
在横竖屏切换的时候,Activity 会重建,在 onStop 之前,和 onPause 没有既定的时序关系,会调用 onSaveInstanceState(Bundle bundle) 方法,其中有一个 Bundle 对象可以用来存储数据,该对象便是 onCreate 中的 Bundle 对象 savedInstancesState。在 onCreate 取得时候要注意判空,而在 onRestoreInstanceState 里面则不需要判空,onRestoreInstanceState 方法调用的时机是在 onStart 之后。
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
同时,我们知道,在 onSaveInstanceState 和 onRestoreInstanceState 方法中,系统自动为我们做了一定的恢复工作。当 Activity 在异常情况下需要重新创建,系统会默认为我们保持当前 Activity 的视图结构,并且在 Activity 重启后为我们恢复这些数据,比如文本框中用户输入的数据、ListView 滚动的位置等等。具体针对某一个特定的 View 系统能为什么恢复那些数据,可以查看 View 的源码。和 Activity 一样,每个 View 都有 onSaveInstanceState 和 onRestoreInstanceState 这两个方法。
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
关于保存和恢复 View 层次结构,系统的工作流程是这样的:首先 Activity 被意外终止时,Activity 会调用 onSaveInstanceState 去保存数据,然后 Activity 会委托 Window 去保存数据,接着 Window 在委托它上面的顶级容器再去一一通知它的子元素来保存数据,这样整个数据保存过程就完成了。
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
```java
|
|
|
|
|
@Override
|
|
|
|
|
public void onSaveInstanceState(Bundle outState, PersistableBundle outPersistentState) {
|
|
|
|
|
super.onSaveInstanceState(outState, outPersistentState);
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
@Override
|
|
|
|
|
protected void onRestoreInstanceState(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
|
|
|
|
|
super.onRestoreInstanceState(savedInstanceState);
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2. startActivityForResult
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
FirstActivity:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
```java
|
|
|
|
|
public void skip(View view) {
|
|
|
|
|
Intent intent = new Intent(this, SecondActivity.class);
|
|
|
|
|
startActivityForResult(intent, 0x01);
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
@Override
|
|
|
|
|
protected void onActivityResult(int requestCode, int resultCode, @Nullable Intent data) {
|
|
|
|
|
super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data);
|
|
|
|
|
if (requestCode == 0x01 && resultCode == 0x02
|
|
|
|
|
&& data != null) {
|
|
|
|
|
Toast.makeText(this, data.getStringExtra("name"), Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SecondActivity:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
```java
|
|
|
|
|
public void goBack(View view) {
|
|
|
|
|
Intent intent = new Intent();
|
|
|
|
|
intent.putExtra("name", "Omooo");
|
|
|
|
|
setResult(0x02, intent);
|
|
|
|
|
finish();
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
这里需要注意的是,requestCode 一定要为正数,看源码便知。其实 startActivity 内部也是调用 startActivityForResult,然后在 startActivityForResult 的第二个参数 requestCode 传 -1。
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3. onNewIntent
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
```java
|
|
|
|
|
@Override
|
|
|
|
|
protected void onNewIntent(Intent intent) {
|
|
|
|
|
super.onNewIntent(intent);
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
在启动模式那块说过,当启动模式是 singleTask 和 singleTop 的时候,系统不需要重新创建 Activity 的时候会回调 onNewIntent 方法。
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4. onConfigurationChanged
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
前面说过,当 Activity 横竖屏切换的时候会导致 Activity 销毁并重建,哪有什么方法能避免呢?其实可以在 AndroidManifest 里面指定 android:configChanges="orientation/screenSize" 来避免重建,这时就会调用 onConfigurationChanged 方法。
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
如果按上面的配置,当字体发生变化时,也会销毁重建,但是不会回调 onConfigurationChanged 方法,所以说想要监听的变化必须要包含之内。
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
```java
|
|
|
|
|
@Override
|
|
|
|
|
public void onConfigurationChanged(Configuration newConfig) {
|
|
|
|
|
super.onConfigurationChanged(newConfig);
|
|
|
|
|
if (newConfig.orientation == Configuration.ORIENTATION_PORTRAIT) {
|
|
|
|
|
//竖屏
|
|
|
|
|
} else {
|
|
|
|
|
//横屏
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5. onTrimMemory
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
```java
|
|
|
|
|
@Override
|
|
|
|
|
public void onTrimMemory(int level) {
|
|
|
|
|
super.onTrimMemory(level);
|
|
|
|
|
if (level == TRIM_MEMORY_UI_HIDDEN) {
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
当内存紧张时会回调,它在 onStop 回调之前。指导应用程序在不同的情况下进行自身的内存释放,以避免被系统直接杀掉,提高应用程序的用户体验。它和 onLowMemory 相比,它有一个 level 评级,onLowMemory 能兼容更低的版本。
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#### 转场动画
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. overridePendingTransition(int enterAnim,int exitAnim)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
需要注意,在 startActivity 和 finish 之后调用。
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2. 设置 Application style
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3. ActivityOptions
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#### 启动流程
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Activity 的启动流程可以分为三个部分:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. Launcher 请求 AMS 过程
|
|
|
|
|
2. AMS 到 ApplicationThread 的调用过程
|
|
|
|
|
3. ActivityThread 启动 Activity
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#### 参考
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
《Android 开发艺术探索》
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
[Android面试官装逼失败之:Activity的启动模式](https://juejin.im/post/59b0f25551882538cb1ecae1)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
[Github项目解析(九)-->实现Activity跳转动画的五种方式](https://blog.csdn.net/qq_23547831/article/details/51821159)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
[https://github.com/HellForGate/TransitionDemo](https://github.com/HellForGate/TransitionDemo)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|