You can not select more than 25 topics
Topics must start with a letter or number, can include dashes ('-') and can be up to 35 characters long.
473 lines
17 KiB
473 lines
17 KiB
---
|
|
APT
|
|
---
|
|
|
|
#### 目录
|
|
|
|
1. 思维导图
|
|
2. 概述
|
|
3. 实现原理
|
|
4. APT
|
|
- Processor
|
|
- init
|
|
- getSupportedAnnotationTypes
|
|
- getSupportedSourceVersion
|
|
- process
|
|
- Element
|
|
- TypeElement
|
|
- ExecutableElement
|
|
- VariableElement
|
|
- RoundEnvironment
|
|
- getElementsAnnotatedWith(BindView.class)
|
|
5. AutoService
|
|
6. JavaPoet
|
|
7. ButterKnife 的实现
|
|
- APT
|
|
- AutoService
|
|
- JavaPoet
|
|
8. 参考
|
|
|
|
#### 思维导图
|
|
|
|
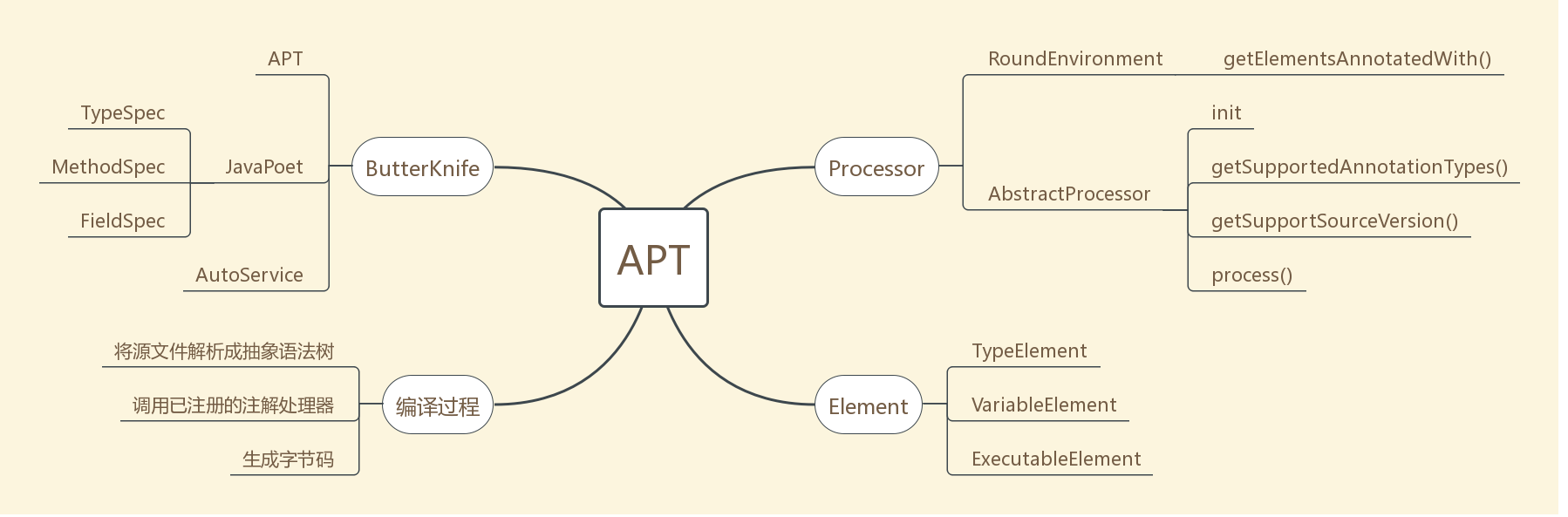
|
|
|
|
#### 概述
|
|
|
|
APT 即注解处理器,它有三个主要用途:一是定义编译规则,并检查被编译的源文件;二是修改已有的源代码;三是生成新的源代码;其中,第二种涉及了 Java 编译器的内部 API,可以会存在兼容性问题,所以并不推荐,第三种较为常见。
|
|
|
|
这节用 APT、JavaPoet、AutoService 实现简单的 ButterKnife,APT 负责处理编译时注解,JavaPoet 用于生成 Java 代码,AutoService 负责注册注解处理器。
|
|
|
|
#### 实现原理
|
|
|
|
在介绍注解处理器之前,我们先来了解一下 Java 编译器的工作流程。
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
如上图所示,Java 源代码的编译过程可以分为三个步骤:
|
|
|
|
1. 将源文件解析成抽象语法树
|
|
2. 调用已注册的注解处理器
|
|
3. 生成字节码
|
|
|
|
如果在第二步调用注解处理器过程中生成了新的源文件,那么编译器将重复第一二步骤,解析并处理新生成的源文件。
|
|
|
|
所以可以这样理解,我们写的自定义注解处理器是给编译器写的,让它按照我们的逻辑来处理注解,所以也得向编译器注册注解处理器。
|
|
|
|
#### APT 注解处理器
|
|
|
|
APT(Annotation Processing Tool)即注解处理器,是一种注解处理工具,用来在编译器扫描和处理注解,通过注解来生成 Java 文件。即以注解作为桥梁,通过预先规定好的代码生成规则来自动生成 Java 文件。此类注解框架的代表有 ButterKnife、Dagger2、EventBus 等。
|
|
|
|
Java API 已经提供了扫描源码并解析注解的框架,开发者可以通过继承 AbstractProcessor 类来实现自己的注解处理逻辑。APT 的原理是在注解了某些代码元素(如字段、函数、类等)后,在编译时编译器会检查 AbstractProcessor 的子类,并且自动调用其 process() 方法,然后将添加了指定注解的所有代码元素作为参数传递给该方法,开发者在根据注解元素在编译期输出对应的 Java 代码。
|
|
|
|
##### Processor
|
|
|
|
所有的注解处理器都需要实现接口 Processor,AbstractProcessor 也是实现了该接口,对开发者更友好。
|
|
|
|
```java
|
|
public interface Processor {
|
|
|
|
void init(ProcessingEnvironment processingEnv);
|
|
|
|
Set<String> getSupportedAnnotationTypes();
|
|
|
|
SourceVersion getSupportedSourceVersion();
|
|
|
|
boolean process(Set<? extends TypeElement> annotations, RoundEnvironment roundEnv);
|
|
|
|
...
|
|
}
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
它有四个重要方法,其中 init 方法用于存放注解处理器的初始化代码,之所以不用构造器,是因为在 Java 编译器中,注解处理器的实例是通过反射 API 生成的,也正是因为使用反射 API,每个注解处理器类都需要定义一个无参构造器。
|
|
|
|
通常来说,当编写注解处理器时,我们不声明任何构造器,并依赖于 Java 编译器,而具体的初始化代码,则放入 init 方法之中。
|
|
|
|
而剩下的三个方法中,getSupportedAnnotationTypes 方法将返回注解处理器所支持的注解类型,这些注解类型只需要用字符串形式表示即可。
|
|
|
|
getSupportedSourceVersion 方法将返回该处理器所支持的 Java 版本,通常直接返回 SourceVersion.latestSupported(),而 process 方法则是最为关键的注解处理方法。
|
|
|
|
process 方法接收两个参数,分别代表该注解处理器所能处理的注解类型,以及囊括当前轮生成的抽象语法树的 RoundEnvironment。
|
|
|
|
通常我们这样使用 RoundEnvironment:
|
|
|
|
```java
|
|
for (Element element : env.getElementsAnnotatedWith(BindView.class)) {
|
|
//todo
|
|
}
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
这个 Element 表示一个程序元素,可以是包、类、或者方法,所有通过注解取得的元素都将以 Element 类型处理,准确来说是 Element 对象的子类处理。
|
|
|
|
Element 的子类:
|
|
|
|
- ExecutableElement
|
|
|
|
表示某个类或接口的方法、构造方法或初始化程序,包括注释类型元素。
|
|
|
|
对应注解是 ElementType.METHOD 和 ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR。
|
|
|
|
- PackageElement
|
|
|
|
表示一个包程序元素,提供对有关包及其成员的信息访问。
|
|
|
|
对应注解是 ElementType.PACKAGE。
|
|
|
|
- TypeElement
|
|
|
|
表示一个类或接口程序元素,提供对有关类型及其成员的信息访问。
|
|
|
|
对应注解是 ElementType.TYPE。
|
|
|
|
注意:枚举类型是一种类,而注解类型是一种接口。
|
|
|
|
- TypeParameterElement
|
|
|
|
表示类、接口、方法元素的类型参数。
|
|
|
|
对应注解是 ElementType.PARAMETER。
|
|
|
|
- VariableElement
|
|
|
|
表示一个字段、enum 常量、方法或构造方法参数、局部变量或异常参数。
|
|
|
|
对应注解是 ElementType.FIELD 和 ElementType.LOCAL_VARIABLE。
|
|
|
|
**不同类型的 Element 的信息获取方式不同。**
|
|
|
|
```java
|
|
@AutoService(Processor.class)
|
|
public class InfoProcessor extends AbstractProcessor {
|
|
|
|
private Elements mElementsUtils;
|
|
|
|
@Override
|
|
public synchronized void init(ProcessingEnvironment processingEnvironment) {
|
|
super.init(processingEnvironment);
|
|
mElementsUtils = processingEnvironment.getElementUtils();
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
@Override
|
|
public boolean process(Set<? extends TypeElement> set, RoundEnvironment roundEnvironment) {
|
|
|
|
//解析类上的注解
|
|
for (Element element : roundEnvironment.getElementsAnnotatedWith(Info.class)) {
|
|
TypeElement classElement = (TypeElement) element;
|
|
PackageElement packageElement = (PackageElement) element.getEnclosingElement();
|
|
//全类名
|
|
System.out.println(classElement.getQualifiedName().toString());
|
|
//类名
|
|
System.out.println(classElement.getSimpleName().toString());
|
|
//包名
|
|
System.out.println(packageElement.getQualifiedName().toString());
|
|
//父类名
|
|
System.out.println(classElement.getSuperclass().toString());
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
//解析方法上的注解
|
|
for (Element element : roundEnvironment.getElementsAnnotatedWith(Info.class)) {
|
|
ExecutableElement executableElement = (ExecutableElement) element;
|
|
TypeElement classElement = (TypeElement) executableElement.getEnclosingElement();
|
|
PackageElement packageElement = mElementsUtils.getPackageOf(classElement);
|
|
//全类名
|
|
String fullClassName = classElement.getQualifiedName().toString();
|
|
//与上面一致
|
|
//...
|
|
//方法名
|
|
String methodName = executableElement.getSimpleName().toString();
|
|
|
|
//方法参数列表
|
|
List<? extends VariableElement> methodParameters = executableElement.getParameters();
|
|
List<String> types = new ArrayList<>();
|
|
for (VariableElement variableElement : methodParameters) {
|
|
TypeMirror methodParameterType = variableElement.asType();
|
|
if (methodParameterType != null) {
|
|
TypeVariable typeVariable = (TypeVariable) methodParameterType;
|
|
methodParameterType = typeVariable.getUpperBound();
|
|
}
|
|
//参数名
|
|
String parameterName = variableElement.getSimpleName().toString();
|
|
//参数类型
|
|
String parameteKind = methodParameterType.toString();
|
|
types.add(methodParameterType.toString());
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
//解析属性上的注解
|
|
for (Element element : roundEnvironment.getElementsAnnotatedWith(Info.class)) {
|
|
VariableElement variableElement = (VariableElement) element;
|
|
TypeElement classElement = (TypeElement) element.getEnclosingElement();
|
|
PackageElement packageElement = mElementsUtils.getPackageOf(classElement);
|
|
//类名
|
|
String className = classElement.getSimpleName().toString();
|
|
//与上面一致
|
|
//...
|
|
|
|
//类成员类型
|
|
TypeMirror typeMirror = variableElement.asType();
|
|
String type = typeMirror.toString();
|
|
}
|
|
return true;
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
##### AbstractProcessor
|
|
|
|
实现一个注解处理器,需要继承 AbstractProcessor ,如下:
|
|
|
|
```java
|
|
public class BindViewProcessor extends AbstractProcessor {
|
|
|
|
private Elements mElementsUtils;
|
|
private Types mTypesUtils;
|
|
private Filter mFilter;
|
|
private Messager mMessager;
|
|
|
|
/**
|
|
* 初始化方法
|
|
* 可以初始化一些给注解处理器使用的工具类
|
|
*/
|
|
@Override
|
|
public synchronized void init(ProcessingEnvironment processingEnvironment) {
|
|
super.init(processingEnvironment);
|
|
mElementsUtils = processingEnvironment.getElementUtils();
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
/**
|
|
* 指定目标注解对象
|
|
*/
|
|
@Override
|
|
public Set<String> getSupportedAnnotationTypes() {
|
|
Set<String> hashSet = new HashSet<>();
|
|
hashSet.add(BindView.class.getCanonicalName());
|
|
return hashSet;
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
/**
|
|
* 指定使用的 Java 版本
|
|
*/
|
|
@Override
|
|
public SourceVersion getSupportedSourceVersion() {
|
|
return SourceVersion.latestSupported();
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
/**
|
|
* 处理注解
|
|
*/
|
|
@Override
|
|
public boolean process(Set<? extends TypeElement> set, RoundEnvironment roundEnvironment) {
|
|
//...
|
|
return true;
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
对于 APT,其实主要是有很多 API 不熟悉。
|
|
|
|
Elements:用于处理程序元素的工具类;
|
|
|
|
Types:用于处理类型数据的工具类;
|
|
|
|
Filter:用于给注解处理器创建文件;
|
|
|
|
Messager:用于给注解处理器报告错误、警告、提示等信息。
|
|
|
|
#### AutoServcie 注册注解处理器
|
|
|
|
以前要注册注解处理器要在 module 的 META_INFO 目录新建 services 目录,并创建一个名为 Java.annotation.processing.Processor 的文件,然后在文件中写入要注册的注解处理器的全民。
|
|
|
|
后来 Google 推出了 AutoService 注解库来实现注册注解处理器的注册,通过在注解处理器上加上 @AutoService(Processor.class) 注解,即可在编译时生成 META_INFO 信息。
|
|
|
|
```java
|
|
@AutoService(Processor.class)
|
|
public class BindViewProcessor extends AbstractProcessor {
|
|
}
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
#### JavaPoet 生成 Java 代码
|
|
|
|
JavaPoet 中有几个常用的类:
|
|
|
|
MethodSpec:代表一个构造方法或方法声明;
|
|
|
|
TypeSpec:代表一个类、接口、或者枚举声明;
|
|
|
|
FieldSpec:代表一个成员变量、字段声明;
|
|
|
|
JavaFile:包含一个顶级类的 Java 文件;
|
|
|
|
关于它的使用,直接看官方文档即可:
|
|
|
|
[https://github.com/square/javapoet](https://github.com/square/javapoet)
|
|
|
|
#### ButterKnife 的实现
|
|
|
|
分为四步:
|
|
|
|
1. 定义注解
|
|
2. 注解处理器处理注解
|
|
3. 生成 Java 文件
|
|
4. 引入
|
|
|
|
##### 定义注解
|
|
|
|
```java
|
|
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.CLASS)
|
|
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
|
|
public @interface BindView {
|
|
int value();
|
|
}
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
##### 注解处理器处理注解、生成 Java 文件
|
|
|
|
```java
|
|
@AutoService(Processor.class)
|
|
public class BindViewProcessor extends AbstractProcessor {
|
|
|
|
private Elements mElementsUtils;
|
|
private Types mTypesUtils;
|
|
private Filter mFilter;
|
|
private Messager mMessager;
|
|
|
|
/**
|
|
* 初始化方法
|
|
* 可以初始化一些给注解处理器使用的工具类
|
|
*/
|
|
@Override
|
|
public synchronized void init(ProcessingEnvironment processingEnvironment) {
|
|
super.init(processingEnvironment);
|
|
mElementsUtils = processingEnvironment.getElementUtils();
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
/**
|
|
* 指定目标注解对象
|
|
*/
|
|
@Override
|
|
public Set<String> getSupportedAnnotationTypes() {
|
|
Set<String> hashSet = new HashSet<>();
|
|
hashSet.add(BindView.class.getCanonicalName());
|
|
return hashSet;
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
/**
|
|
* 指定使用的 Java 版本
|
|
*/
|
|
@Override
|
|
public SourceVersion getSupportedSourceVersion() {
|
|
return SourceVersion.latestSupported();
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
/**
|
|
* 处理注解
|
|
*/
|
|
@Override
|
|
public boolean process(Set<? extends TypeElement> set, RoundEnvironment roundEnvironment) {
|
|
//获取所有包含 BindView 注解的元素
|
|
Set<? extends Element> elementSet = roundEnvironment.getElementsAnnotatedWith(BindView.class);
|
|
Map<TypeElement, Map<Integer, VariableElement>> typeElementMapHashMap = new HashMap<>();
|
|
for (Element element : elementSet) {
|
|
//因为 BindView 的作用对象是 FIELD,因此 element 可以直接转化为 VariableElement
|
|
VariableElement variableElement = (VariableElement) element;
|
|
//getEnclosingElement 方法返回封装此 Element 的最里层元素
|
|
//如果 Element 直接封装在另一个元素的声明中,则返回该封装元素
|
|
//此处表示的即是 Activity 类对象
|
|
TypeElement typeElement = (TypeElement) variableElement.getEnclosingElement();
|
|
Map<Integer, VariableElement> variableElementMap = typeElementMapHashMap.get(typeElement);
|
|
if (variableElementMap == null) {
|
|
variableElementMap = new HashMap<>();
|
|
typeElementMapHashMap.put(typeElement, variableElementMap);
|
|
}
|
|
//获取注解的值,即 ViewId
|
|
BindView bindAnnotation = variableElement.getAnnotation(BindView.class);
|
|
int viewId = bindAnnotation.value();
|
|
variableElementMap.put(viewId, variableElement);
|
|
}
|
|
for (TypeElement key : typeElementMapHashMap.keySet()) {
|
|
Map<Integer, VariableElement> elementMap = typeElementMapHashMap.get(key);
|
|
String packageName = ElementUtil.getPackageName(mElementsUtils, key);
|
|
JavaFile javaFile = JavaFile.builder(packageName, generateCodeByPoet(key, elementMap)).build();
|
|
try {
|
|
javaFile.writeTo(processingEnv.getFiler());
|
|
} catch (IOException e) {
|
|
e.printStackTrace();
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
return true;
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
/**
|
|
* 生成 Java 类
|
|
*
|
|
* @param typeElement 注解对象的上层元素对象,即 Activity 对象
|
|
* @param variableElementMap Activity 包含的注解对象以及注解的目标对象
|
|
* @return
|
|
*/
|
|
private TypeSpec generateCodeByPoet(TypeElement typeElement, Map<Integer, VariableElement> variableElementMap) {
|
|
//自动生成的文件以 Activity 名 + ViewBinding 进行命名
|
|
return TypeSpec.classBuilder(ElementUtil.getEnclosingClassName(typeElement) + "ViewBinding")
|
|
.addModifiers(Modifier.PUBLIC)
|
|
.addMethod(generateMethodByPoet(typeElement, variableElementMap))
|
|
.build();
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
/**
|
|
* 生成方法
|
|
*
|
|
* @param typeElement 注解对象上层元素对象,即 Activity 对象
|
|
* @param variableElementMap Activity 包含的注解对象以及注解的目标对象
|
|
* @return
|
|
*/
|
|
private MethodSpec generateMethodByPoet(TypeElement typeElement, Map<Integer, VariableElement> variableElementMap) {
|
|
ClassName className = ClassName.bestGuess(typeElement.getQualifiedName().toString());
|
|
//方法参数名
|
|
String parameter = "_" + StringUtil.toLowerCaseFirstChar(className.simpleName());
|
|
MethodSpec.Builder methodBuilder = MethodSpec.methodBuilder("bind")
|
|
.addModifiers(Modifier.PUBLIC, Modifier.STATIC)
|
|
.returns(void.class)
|
|
.addParameter(className, parameter);
|
|
for (int viewId : variableElementMap.keySet()) {
|
|
VariableElement element = variableElementMap.get(viewId);
|
|
//被注解的字段名
|
|
String name = element.getSimpleName().toString();
|
|
//被注解的字段的对象类型的全名称
|
|
String type = element.asType().toString();
|
|
String text = "{0}.{1}=({2})({3}.findViewById({4}));\n";
|
|
methodBuilder.addCode(MessageFormat.format(text, parameter, name, type, parameter, String.valueOf(viewId)));
|
|
}
|
|
return methodBuilder.build();
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
##### 引入
|
|
|
|
```java
|
|
public class ButterKnife {
|
|
public static void bind(Activity activity) {
|
|
Class clazz = activity.getClass();
|
|
try {
|
|
Class bindViewClass = Class.forName(clazz.getName() + "ViewBinding");
|
|
Method method = bindViewClass.getMethod("bind", clazz);
|
|
method.invoke(null, activity);
|
|
} catch (Exception e) {
|
|
e.printStackTrace();
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#### 参考
|
|
|
|
[注解处理器](https://time.geekbang.org/column/article/40189)
|
|
|
|
[教你实现一个轻量级的注解处理器 APT](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/3zrAzOUGpovRRbuYnce3uw)
|
|
|
|
[拆 JakeWharton 系列之 ButterKnife](https://juejin.im/post/58f388d1da2f60005d369a09)
|
|
|
|
[ButterKnife原理分析(二)注解的处理](https://www.jianshu.com/p/bcddc376c0ef)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|