17 KiB
目录
- 前言
- 基础知识储备
- 坐标系
- 颜色
- 自定义 View
- 分类和流程
- Canvas 之常用 API
- MotionEvent
- 手势检测
- 常见问题汇总
- 处理 warp_content
- 处理 padding
- 处理 margin
- 实战之酷炫进度条
- 参考
前言
自定义 View 系列直接看 GcsSloop 自定义 View 系列 就可以了,熟悉了 API 能自定义简单的 View,该系列最后都一个例子来练习,可以参考 https://github.com/Omooo/ChartsDemo 中的代码,没错,也是我的~
这些知识长时间不实践就忘的差不多了,于是再来一遍。
基础知识储备
坐标系
Android 中的屏幕坐标系是以屏幕的左上角为坐标原点的,向右为 x 正轴,向下是 y 正轴。
这里就要提一下 View 的坐标系了,View 的坐标系统是相对于父控件而言的:
getTop() //获取子 View 左上角到父 View 顶部的距离
getLeft() //获取子 View 左上角到父 View 左边的距离
getBottom() //获取子 View 右下角到父 View 顶部的距离
getRight() //获取子 View 右上角到父 View 左边的距离
getBottom() - getTop() = View 的高
getRight() - getLeft() = View 的宽
MotionEvent 中的 getXxx 和 getRawXxx 的区别:
event.getX() //触摸点相对于其所在 View 坐标系的坐标
event.getY()
event.getRawX() //触摸点相对于屏幕坐标系的坐标
event.getRawY()
颜色
Android 支持的颜色模式有:
| 颜色模式 | 备注 |
|---|---|
| ARGB8888 | 四通道高精度(32位) |
| ARGB4444 | 四通道低精度(16位) |
| RGB565 | 屏幕默认模式(16位) |
RGB 代表红绿蓝三原色,A 代表透明度,后面的数值表示该类型用多少位二进制来描述。
#f00 //低精度 - 不带透明通道红色
#af00 //低精度 - 带透明通道红色
#ff0000 //高精度 - 不带透明通道红色
#aaff0000 //高精度 - 带透明通道红色
有了基础知识储备,接下来就开始进入自定义 View 了~~~
自定义 View 分类和流程
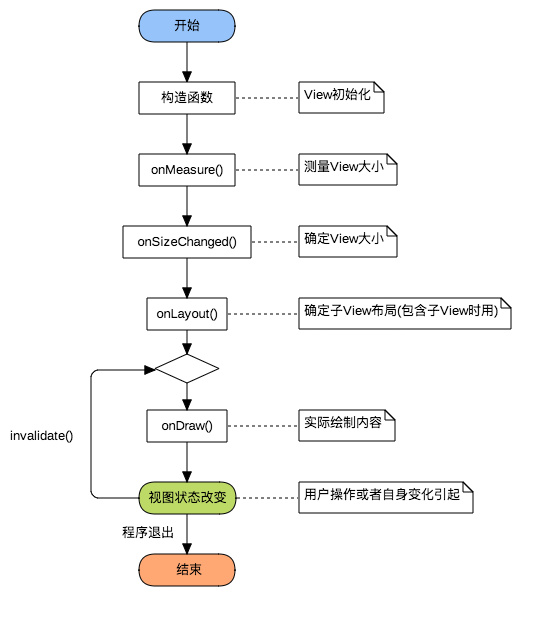
自定义 View 可以分为两类:一类是自定义 ViewGroup,另一种是自定义 View。自定义 ViewGroup 一般是利用已有的 View 按照特定的布局方式来实现新的组件,比如带自动换行的水平的线性布局等。自定义 View 一般是由于没有现成的 View 可以使用,需要自己实现 onDraw 来绘制。
自定义 View 的流程也是一个通用的套路:
构造函数
public class MyCustomView extends View {
//在 Activity 中以 new MyCustomView(this) 创建 View
public MyCustomView(Context context) {}
//在 xml 中创建 View
public MyCustomView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) {}
//为 View 指定样式
public MyCustomView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {}
//API > 21
public MyCustomView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr, int defStyleRes) {}
我们只需要实现前两个构造函数即可,AttributeSet 用于获取自定义属性等。
onMeasure()
用于测量 View 的大小。
你可能会问,既然我们在 xml 里面可以指定 View 的宽高尺寸,为什么还需要自己测量呢?
这是因为,View 的大小不仅由自身所决定,同时也会受父控件的影响,比如我们设置 warp_content 或 match_parent。
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
//获取宽度尺寸和宽度测量模式
int widthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
setMeasuredDimension(widthSize, heightSize);
}
onMeasure 中的参数可以翻译成测量规格,它有两部分组成:宽高实际尺寸和宽高测量模式。
测量模式有三种:
| 模式 | 二进制值 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| UNSPECIFIED | 00 | 默认值,父控件没有给子 View 任何限制,子 View 可以设置为任意大小,一般用在系统中,我们可以不管 |
| EXACTLY | 01 | 表示父控件已经确切指定了子 View 的大小,对应于 match_parent 和 确切数值 100dp |
| AT_MOST | 10 | 表示子 View 的大小存在上限,一般是父 View 大小,对应于 warp_content |
所以在测量规格中,只需要两个 bit 就能表示完测量模式,而事实上正是这样做的,测量规格是一个 int 数值,32位,前两位表示测量模式,后三十位表示测量数值。
onSizeChanged()
在视图大小发生改变时调用。
既然在测量完 View 并使用 setMeasuredDimension 函数之后 View 的大小基本上已经确定了,那为什么还要再次确认 View 的大小呢?
这是因为 View 的大小不仅由 View 本身控制,而且受父控件的影响,所以我们在确定 View 大小的时候最好使用系统提供的 onSizedChanged 回调函数。
protected void onSizeChanged(int w, int h, int oldw, int oldh) {
super.onSizeChanged(w, h, oldw, oldh);
}
w、h 即是 View 最终的大小。
onLayout()
确定布局的函数是 onLayout,它用于确定子 View 的位置,在定义 ViewGroup 中会用到,它调用的是子 View 的 layout 函数。
在自定义 ViewGroup 中,onLayout 一般是循环取出子 View,然后经过计算得出各个子 View 位置的坐标值,然后用以下函数设置子 View 位置。
child.layout(l,t,r,b)
onDraw()
onDraw 是实际绘制的部分,使用 Canvas 绘制。
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
}
自定义 View 之 Canvas 常用 API
| 操作类型 | 相关 API | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| 绘制颜色 | drawColor、drawRGB、drawARGB | 使用单一颜色填充整个画布 |
| 绘制基本图形 | drawPoint、drawPoints、drawLine、drawLines、drawRect、drawRoundRect、drawOval、drawCircle、drawArc | 绘制点、线、矩形、圆角矩形、椭圆、圆、圆弧 |
| 绘制图片 | drawBitmap、drawPicture | 绘制位图和图片 |
| 绘制路径 | drawPath | 绘制路径,绘制贝塞尔曲线 |
| 画布裁剪 | clipPath、clipRect | 设置画布的显示区域 |
| 画布变换 | translate、scale、rotate、skew | 位移、缩放、旋转、错切 |
MotionEvent
| 事件 | 简介 |
|---|---|
| ACTION_DOWN | 手指初次接触屏幕时触发 |
| ACTION_MOVE | 手指在屏幕上滑动时触发,会多次触发 |
| ACTION_UP | 手指离开屏幕时触发 |
| ACTION_CANCEL | 事件被上层拦截时触发 |
这里主要说下 ACTION_CANCEL,它的触发条件是事件被上层拦截。但是我们知道,在事件分发中,如果父 View 拦截了事件,那么子 View 是收不到任何事件的。所以这个 ACTION_CANCEL 的正确触发条件是:
只有父 View 回收事件处理权的时候,子 View 才会收到一个 ACTION_CANCEL 事件。
举个例子:
上层 View 是一个 RecyclerView,它收到了一个 ACTION_DOWN 事件,由于这可能是个点击事件,所以它先传递给了对应的 ItemView,询问 ItemView 是否需要这个事件,然后接下来又传递过来一个 ACTION_MOVE 事件,且移动的方向和 RecyclerView 的可滑动方向一致,这时候 RecyclerView 判断这个事件是滚动事件,于是要回收事件处理权,这时候对应的 ItemView 就会收到一个 ACTION_CANCEL,并且不会再收到后续事件。
手势检测(GestureDetector)
GestureDetector 可以使用 MotionEvents 检测各种手势和事件,使用起来也很简单~
final GestureDetector detector = new GestureDetector(this, new GestureDetector.SimpleOnGestureListener() {
@Override
public boolean onDoubleTap(MotionEvent e) {
Toast.makeText(WidgetActivity.this, "双击事件", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
return super.onDoubleTap(e);
}
});
mButton.setOnTouchListener(new View.OnTouchListener() {
@Override
public boolean onTouch(View v, MotionEvent event) {
return detector.onTouchEvent(event);
}
});
常见问题汇总
处理 warp_content
-
自定义 View 的处理
如果我们不处理自定义 View 中的 warp_content,那么它和 match_parent 的效果一样。这里我们需要在 onMeasure() 里面做特殊处理:
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) { //获取宽度尺寸和宽度测量模式 int widthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec); int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec); int heightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec); int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec); int defaultWidth = 200; //默认值 int defaultHeight = 200; setMeasuredDimension(widthSize, heightSize); if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST && heightMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) { setMeasuredDimension(defaultWidth, defaultHeight); } else if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) { setMeasuredDimension(defaultWidth, heightSize); } else if (heightMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) { setMeasuredDimension(widthSize, defaultHeight); } }可以看到,其实我们只是当是 warp_content 的时候设置一个默认值,但是这样不灵活,我们可以在自定义属性中设置。其次,我们可以参考系统对 TextView 的设置,它会根据文字的大小来设置默认宽高。
-
自定义 ViewGroup 的处理
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) { super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec); //将所有的子 View 进行测量,这会触发每个子 View 的 onMeasure //measureChild 是对单个 View 进行测量 measureChildren(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec); int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec); int widthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec); int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec); int heightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec); int childCount = getChildCount(); if (childCount == 0) { setMeasuredDimension(0, 0); } else { if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST && heightMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) { int height = getTotalHeight(); //获取子 View 高度加和 int width = getMaxChildWidth(); //获取子 View 的最大宽度 setMeasuredDimension(width, height); } else if (heightMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) { setMeasuredDimension(widthSize, getTotalHeight()); } else if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) { setMeasuredDimension(getMaxChildWidth(), heightSize); } } }这里我们以自定义一个垂直的线性布局为例,当 ViewGroup 是 warp_content 的时候,高度为子 View 的高度和,宽度为子 View 中的最大宽度。
处理 padding
-
自定义 View 的处理
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) { mPaint.setColor(Color.RED); Rect rect = new Rect(0, 0, 100, 100); Rect rect1 = new Rect(0 + getPaddingLeft(), 0 + getPaddingTop(), 100 - getPaddingRight(), 100 - getPaddingBottom()); canvas.drawRect(rect, mPaint); } -
自定义 ViewGroup 的处理
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) { super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec); //将所有的子 View 进行测量,这会触发每个子 View 的 onMeasure //measureChild 是对单个 View 进行测量 measureChildren(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec); int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec); int widthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec); int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec); int heightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec); //获取子 View 高度加和 padding 值 int height = getTotalHeight() + getPaddingTop() + getPaddingBottom(); //获取子 View 的最大宽度加 padding 值 int width = getMaxChildWidth() + getPaddingLeft() + getPaddingRight(); int childCount = getChildCount(); if (childCount == 0) { setMeasuredDimension(0, 0); } else { if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST && heightMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) { setMeasuredDimension(Math.min(width, widthSize), Math.min(height, heightSize)); } else if (heightMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) { setMeasuredDimension(widthSize, Math.min(height, heightSize)); } else if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) { setMeasuredDimension(Math.min(width, widthSize), heightSize); } } }
处理 margin
自定义 View 里 margin 是生效的,无需处理,只有 ViewGroup 才需要处理 margin。
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
int count = getChildCount();
int currentHeight = t;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
int height = child.getMeasuredHeight();
int width = child.getMeasuredWidth();
child.layout(l + lp.leftMargin, currentHeight + lp.topMargin, l + width + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin, currentHeight + height + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin);
currentHeight += height;
}
}
@Override
public LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs) {
return new MarginLayoutParams(getContext(), attrs);
实战
public class MyProgressView extends View {
private Paint mPaint;
private int mWidth;
private int mHeight;
private int textPadding = 5;
private int progress = 0;
public MyProgressView(Context context) {
super(context);
initPaint();
}
public MyProgressView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
initPaint();
}
private void initPaint() {
mPaint = new Paint();
mPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
mPaint.setStrokeWidth(3);
mPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.FILL);
mPaint.setTextSize(14);
}
@Override
protected void onSizeChanged(int w, int h, int oldw, int oldh) {
super.onSizeChanged(w, h, oldw, oldh);
mWidth = w;
mHeight = h;
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
String text = progress + "%";
float textWidth = mPaint.measureText(text) + textPadding;
Rect rect = new Rect();
mPaint.getTextBounds(text, 0, text.length(), rect);
mPaint.setColor(Color.BLUE);
canvas.drawLine(0, mHeight / 2, progress * ((mWidth - textWidth) / 100), mHeight / 2, mPaint);
canvas.drawText(text, progress * ((mWidth - textWidth) / 100) + textPadding, (mHeight - rect.height()) / 2 + 2 * textPadding, mPaint);
mPaint.setColor(Color.GRAY);
canvas.drawLine(progress * ((mWidth - textWidth) / 100) + textWidth + textPadding, mHeight / 2, mWidth, mHeight / 2, mPaint);
}
public void setProgress(int progress) {
if (progress > 100) {
progress = 100;
} else if (progress < 0) {
progress = 0;
}
this.progress = progress;
postInvalidate();
}
}